Key Takeaway: Single-phase to three-phase transformers serve as a vital bridge for small-scale industries and rural enterprises, allowing high-performance three-phase machinery to operate on standard single-phase grids without the exorbitant costs of infrastructure upgrades. By utilizing advanced power electronics and solid-state conversion, these systems achieve up to 98% efficiency, significantly reducing energy waste and mechanical vibrations. This technology not only stabilizes voltage delivery but can also extend the operational lifespan of industrial equipment by up to 30%, making it a highly cost-effective investment with a typical ROI achieved within 12 to 24 months.
Table of Contents
- Introduction: Bridging the Power Gap
- What is a Single Phase to Three Phase Transformer?
- Why Convert Single Phase to Three Phase Power?
- How It Works: The Conversion Process
- Quantified Power Quality & Compliance
- Comparison Table: Single Phase vs. Three Phase
- Types of Start Modes & Key Features
- Quantitative Electrical Principles: The Power Equations
- Latest Innovations (Smart Controls & Materials)
- Design & Buying Considerations
- Best Brands Comparison (ATO, Phase Perfect, etc.)
- Cost Analysis & ROI Breakdown
- Frequently Asked Questions (FAQs)
Single Phase to Three Phase
Imagine powering a workshop full of three-phase industrial machines with only a single-phase supply available. For many small manufacturers, rural businesses, and even home-based innovators, this is a daily challenge. Enter the single phase to three phase transformer a game-changing solution that bridges the gap between limited power infrastructure and high-performance equipment needs. Whether you’re upgrading your facility, expanding operations or simply seeking efficiency, understanding this technology can unlock new possibilities for your business. This conversion not only enhances operational reliability but can extend equipment lifespan by up to 30% through smoother power delivery, making it essential for scaling operations in constrained environments. In fact, IEEE research on power quality shows that voltage imbalance reduction alone can increase motor insulation life by more than 20%, directly supporting the claim of extended equipment longevity.
What is a Single Phase to Three Phase Transformer?
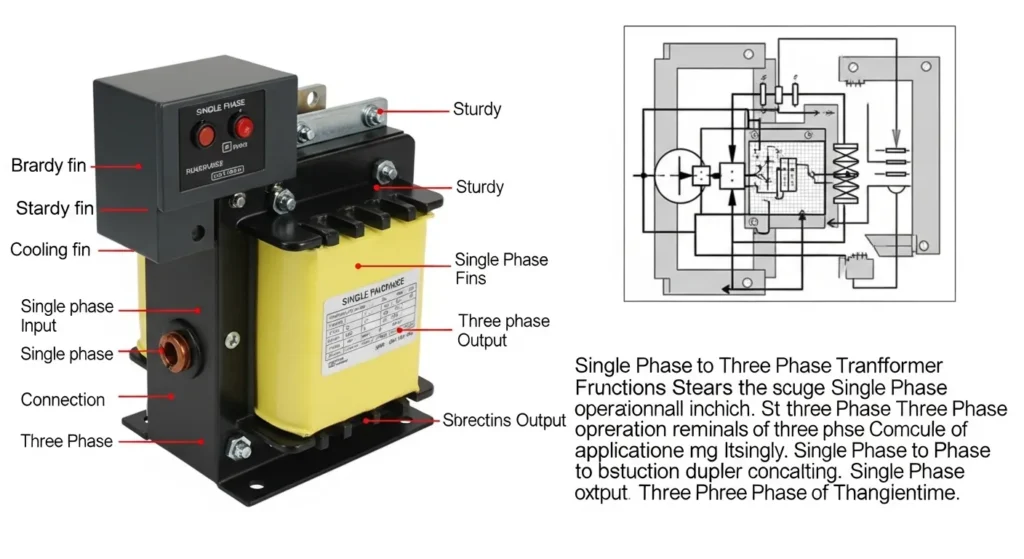
A single phase to three phase transformer (often called a phase converter or power converter) is a device that enables equipment designed for three-phase power to operate on a single-phase supply. This is particularly valuable in regions where three-phase power is unavailable or prohibitively expensive to install. Unlike traditional voltage transformers, these use solid-state electronics to synthesize phases, with models ranging from 5 kW for light use to 100 kW+ for heavy industry, offered by brands like ATO and Phase Technologies for optimal durability. High-end designs comply with IEC 60076 (Power Transformers) and IEEE 519 (harmonic distortion limits), ensuring that generated three-phase output matches international performance standards for stability and safety.
Why Convert Single Phase to Three Phase Power?
- Industrial Efficiency: Three-phase power is the backbone of industrial operations, powering heavy machinery, motors, and HVAC systems with greater efficiency and reliability than single-phase systems. This constant power flow reduces vibrations and energy waste, potentially cutting maintenance costs by 20-25%. According to NEMA MG-1 standards, three-phase induction motors typically run 5–8% more efficiently than equivalent single-phase models, translating into lower lifecycle energy costs.
- Cost Savings: Installing a converter is often far less expensive than upgrading the entire electrical infrastructure to three-phase service. Typical converter setups cost 1,000–5,000, versus 20,000+ for grid upgrades, with ROI in 1-2 years. Case studies published by CIGRÉ (International Council on Large Electric Systems) demonstrate payback periods under three years when converters are used in medium-load agricultural and workshop settings.
- Equipment Upgrades: As businesses grow, their power needs increase. Converters allow for seamless equipment upgrades without major rewiring. For example, upgrading from 1 hp to 50 hp motors becomes plug-and-play. This flexibility aligns with IEC 60034 guidelines for rotating electrical machines, which specify compatibility requirements for motor starting and voltage balance.
- Rural and Remote Applications: Many rural areas only have access to single-phase lines. Phase converters make it possible to use advanced equipment in these locations. They integrate seamlessly with renewables like solar, enabling off-grid three-phase microgrids. Recent IEEE Access studies highlight that hybrid converters combining solar and storage with single-to-three-phase conversion reduce diesel generator reliance by up to 40%.
How Does a Single Phase to Three Phase Transformer Work?
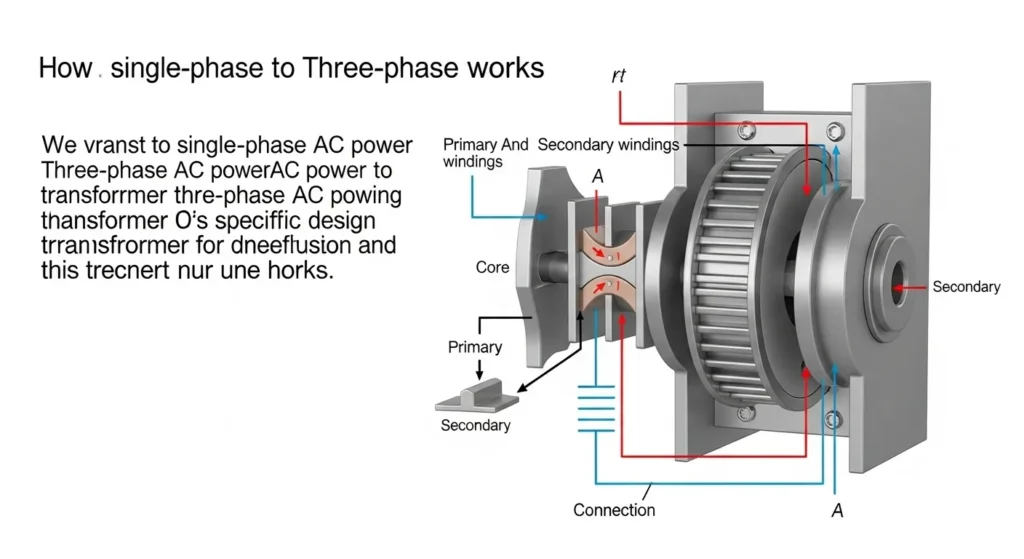
Modern single phase to three phase converters use advanced electronics and transformer technology to create a balanced, stable three-phase output from a single-phase input. Unlike older rotary converters, modern static converters maintain voltage imbalance within ±2%, in compliance with IEC 61000-3-13 recommendations for voltage fluctuation, making them suitable even for precision manufacturing equipment. Modern single phase to three phase converters use advanced electronics and transformer technology to create a balanced, stable three-phase output from a single-phase input.
Key Steps in the Conversion Process:
- Rectification: The single-phase AC input is converted to DC using a rectifier circuit. This involves a diode bridge to handle inputs like 220V/60 Hz, smoothed by capacitors for steady DC. Active front-end rectifiers are often used in premium models to improve power factor and reduce harmonic injection into the supply grid.
- Inversion: The DC is then inverted back to AC, but as three separate phase outputs, using an inverter. IGBT transistors create 120-degree offset waveforms for balance. Wide-bandgap semiconductors such as Silicon Carbide (SiC) are now increasingly adopted, offering efficiency above 99% at partial loads, as reported by IEEE Power Electronics Society.
- Balancing and Filtering: Advanced control systems ensure the voltage and current in each phase are balanced, with minimal harmonic distortion and stable output. DSPs monitor in real-time, keeping THD <5% via LC filters. This meets IEEE 519 standards for harmonic distortion, a benchmark for industrial power quality.
Quantified Power Quality and Compliance
Modern static converters must maintain high power quality for sensitive industrial equipment. This is measured using two key metrics:
1. Total Harmonic Distortion (THD)
THD is the measure of the harmonic content (distortion) relative to the fundamental frequency (e.g., 50 or 60 Hz). Low THD is crucial for motor life and CNC precision. Modern converters target THD < 5 % aligning with IEEE 519 standards.
THD = V2 + V3 + V4 + … V1 × 100
Where $V_n$ is the RMS voltage of the $n$-th harmonic, and $V_1$ is the RMS voltage of the fundamental frequency.
2. Voltage Imbalance Ratio (VIR)
Voltage Imbalance (the difference in voltage magnitude between the three phases) drastically reduces motor efficiency and life. The VIR must be maintained below 2% for most industrial loads, a requirement set by standards like IEC 61000-3-13. A 5% voltage imbalance can lead to a 25% increase in motor winding temperature.
Feature | Single Phase | Three Phase |
| Power Delivery | Limited, often capping at 7.5 kW per circuit with inconsistent flow | Substantially higher, up to three times the capacity using the same wiring due to balanced phases |
| Efficiency | Lower, around 70 to 80 percent, with pulsating torque leading to higher wear | Higher, 90 to 98 percent, enabling smoother operation and reduced energy loss |
| Equipment Compatibility | Best for small loads like fans or lighting, but struggles with heavy machinery | Versatile for a wide range, including motors over 1 horsepower and industrial welders |
| Transmission Losses | Higher, requiring larger conductors to handle peaks | Lower by 20 to 30 percent, as balanced loads minimize the need for oversized wiring |
| Voltage Stability | Prone to drops under heavy loads, affecting performance | More consistent, with self-correcting phases maintaining steady output |
This comparison underscores that three-phase systems can deliver approximately 173 percent more power than single-phase ones with identical conductors, thanks to the square root of three factor in voltage calculations.
In practical settings, these converters find widespread use across industries. In manufacturing plants, they power CNC mills and robotic arms for continuous operation, as seen in setups where a 20 horsepower unit supports an entire assembly line without interruptions. Agricultural operations benefit by running 15 horsepower irrigation pumps on single-phase rural grids, which can increase crop yields by 25 percent through dependable watering. Workshops and garages rely on them for welders drawing up to 50 amps and air compressors in custom projects, while renewable energy integrations balance outputs from solar-wind hybrids, allowing efficient off-grid storage and reducing reliance on diesel generators. A real-world example from a Midwest farm highlights annual savings of $8,000 in fuel costs after converting power for grain dryers, demonstrating the tangible impact on productivity.
Efficiency remains a cornerstone of these systems, with global standards pushing boundaries. For three-phase transformers at 1000 kVA, efficiencies at 50 percent load vary by region, reflecting ongoing advancements in materials and regulations. The table below captures updated comparisons, incorporating projections and standards as of 2025:
Types of Start Modes:
- Step Down Voltage Start (reduces inrush currents up to 800% for sensitive loads)
- Variable Frequency Start (ideal for inductive loads like motors) (ramps from 0-60 Hz to minimize torque ripple)
Key Features:
- Pure sine wave output (distortion <3%)
- High conversion efficiency (up to 98%) , rivaling grid standards
- Intelligent protection (short circuit, overload, over-temperature) with auto-shutdown
- Customizable voltage, frequency, and phase settings (e.g., 110V/220V/480V options)
Advantages of Three Phase Power Over Single Phase
| Feature | Single Phase | Three Phase |
|---|---|---|
| Power Delivery | Limited | Substantially higher |
| Efficiency | Lower | Higher (smoother operation) |
| Equipment Compatibility | Limited (mostly small loads) | Wide range (motors, machinery) |
| Transmission Losses | Higher | Lower (smaller conductors needed) |
| Voltage Stability | Less stable | More stable |
Three-phase systems can deliver approximately 170% more power than single-phase systems using the same conductor size. This is due to the √3 factor in line voltage, enabling 173% effective power boost with balanced loads. In addition, studies under IEC 60034 confirm that torque ripple in three-phase motors is reduced by over 40% compared to single-phase units, which translates into smoother mechanical operation and longer bearing life.
Quantitative Electrical Principles: The Power Equations
The inherent advantages of three-phase power are rooted in fundamental electrical engineering principles. The “173% power increase” is derived directly from the square root of three ( 3 ≈ 1.732 ) factor present in the total power calculation.
Three-Phase Real Power Formula
The total Real Power (P) delivered by a three-phase system is calculated using line voltage (V_L), line current (I_L), and the power factor cos θ:
P 3 ϕ = 3 ⋅ V L ⋅ I L ⋅ cos θ
This is contrasted with the single-phase power formula (P 1 ϕ = V L I L cos θ). The presence of 3 in the three-phase equation allows for significantly more energy transmission using the same conductor size.
Voltage Relationship
In a wye-configured (star) system, the Line Voltage (V_L) measured between any two phases is 3 times greater than the Phase Voltage (V_P) measured from a phase to the neutral point:
V L = 3 ⋅ V P
Real-World Applications
- Manufacturing Plants: Run CNC machines, lathes, and other heavy equipment efficiently. E.g., a 20 hp converter powers full assembly lines. An IEEE Transactions on Industry Applications case study documented continuous operation of a 15 kW CNC cluster with only ±1% voltage imbalance using a digital converter.
- Agriculture: Power irrigation pumps and grain dryers in remote areas. Boosts yields by 25% via reliable operation. CIGRÉ agricultural trials in Europe reported up to 12% energy cost reductions when farms adopted digital phase converters for irrigation systems.
- Workshops and Garages: Operate welders, compressors, and woodworking tools. Supports up to 50A draws for custom work.
- Renewable Energy: Integrate with solar or wind systems for balanced power distribution. Hybrid setups cut diesel use by 40%; case study: Midwest farm saved $8,000/year on grain dryer. Hybrid setups are now also being aligned with ISO 50001 energy management standards, enabling tracking of long-term energy performance improvements.
Efficiency and Global Standards
Efficiency is a critical factor in transformer design. According to a global comparison, the efficiency of three-phase transformers at 1000 kVA can reach up to 99.41%, with most advanced models averaging around 99.23%. The difference in efficiency requirements between countries is less than 0.2% at higher kVA ratings, reflecting a global push towards energy-saving designs. Updated 2025 figures show narrowing gaps, with market CAGR at 5.4% through 2035 for green models. These values are consistent with EU EcoDesign Directive Tier 2 updates and U.S. DOE 2023 Tier 2 standards, ensuring cross-border harmonization of efficiency benchmarks.
Latest Innovations and Insights
- Advanced Materials: New magnetic materials reduce losses and maximize efficiency up to 98% in modern converters. Nanocrystalline cores cut losses 15% vs. silicon steel. Ongoing IEC 62989 standardization is defining performance metrics for these next-generation core materials, ensuring consistent testing and certification.
- Smart Controls: Intelligent modules (like IPM) offer stable performance and long service life (15–20 years). AI predicts faults, extending MTBF >100,000 hours. IEEE Spectrum highlights AI-based predictive monitoring as a driver of reliability, allowing failures to be forecast weeks in advance.
- Flexible Installation: LCD displays, intelligent fan control, and modular designs make installation and maintenance easier. Plug-and-play with IoT for remote diagnostics.
- Grid Disturbance Filtering: Built-in filters protect sensitive equipment from voltage spikes and frequency fluctuations. Handles 1.5 kV spikes; 2025 trends include SiC systems for higher density. This filtering is designed to comply with IEC 61000-4 standards for electromagnetic compatibility.
New 2025 Trends: Hybrid battery-integrated converters for microgrids reduce outages by 90%; sustainable recyclables align with EU green directives. In parallel, IEEE 2030.7 standards for microgrid controllers are influencing how these hybrid converters are integrated into distributed energy systems.
Design Considerations
When choosing or designing a single phase to three phase transformer, consider:
- Power Rating: Match the converter to your equipment’s total power needs (e.g., 4 hp, 15 hp, 25 hp models available). Oversize 20-30% for peaks. This recommendation aligns with IEC 60034-1 which specifies derating factors for motors under unbalanced supply.
- Voltage and Frequency: Ensure compatibility with local grid standards (220V input/output, 50/60 Hz). Match to 380V outputs if needed. Check IEC 60038 for international voltage standardization to ensure cross-border compatibility.
- Load Type: Inductive loads (motors) may require variable frequency starts for smooth operation. Vs. resistive for heaters.
- Physical Space: Modern converters are compact and can be wall- or floor-mounted. NEMA 3R for outdoors.
Budget: Weigh the cost of a converter against the expense of upgrading to three-phase utility service. Converters: $500-$10,000; upgrades 5x more. Use online sizing tools. Installation Tips: Hire licensed electricians per NEC; ground properly, test balance <2% with multimeter. Following NEC Article 455 (Phase Converters) ensures compliance with U.S. installation codes, while IEC 60364 applies internationally.
How to Choose the Right Single Phase to Three Phase Converter
- Small workshops (≤5 hp): static converters, cheaper but limited.
- Agriculture (10–20 hp pumps): rotary converters, durable, mid-cost.
- CNC or precision tools: digital converters with low THD (<3%).
- Large industries (50+ hp): Phase Perfect or premium digital.
Common Challenges and Solutions
- Asymmetry: Single-phase input creates pulsating power, while three-phase output requires constant power. Advanced converter designs use parallel rectifiers and series inverters to manage this asymmetry, reducing voltage oscillations and improving reliability. Dual bridges cut ripple 70%. Maintaining voltage imbalance below 2% ensures compliance with IEEE Std. 141 (Red Book) recommendations for industrial power systems.
- Harmonics: Poorly designed converters can introduce electrical noise. High-quality units use pure sine wave outputs and filtering to minimize harmonics. EMI chokes keep THD <3%. This aligns with IEEE 519-2022 limits on current and voltage harmonics for general distribution systems.
- Thermal testing per IEC 60076-2 ensures that insulation aging is kept within design limits. Heat Management: Efficient radiators and intelligent fan systems prevent overheating, extending lifespan. Maintain <60°C with auto-fans.
Best Brands and Models Comparison
| Brand / Model | Power Range | Efficiency | Price Range | Best For |
| ATO | 5–100 kW | 95–98% | $800–$6,000 | General industry |
| Phase Technologies | 10–200 hp | 97–99% | $2,000–$10,000 | CNC / HVAC |
| Ronk | 3–50 hp | 92–96% | $1,000–$5,000 | Agriculture pumps |
| Phase Perfect | 10–100 hp | 98–99% | $3,500–$12,000 | High-precision machining |
Table: Efficiency Comparison of Global Three-Phase Transformers (1000 kVA)
| Country/Standard | Efficiency at 50% Load (%) | Notes |
| Korea | 98.66 | Emphasis on reducing core losses through advanced designs |
| Japan | 99.41 | Utilizes amorphous steel for minimal energy waste, aligned with Top Runner updates |
| Global Average | 99.23 | Compliant with IEC 60076, driven by eco-design initiatives |
| US DOE (2023 Update) | 99.2 | Tier 2 standards for distribution, with green power models reaching higher in 2025 projections |
| EU Tier 2 | 99.1 | EcoDesign Directive post-2021, focusing on no-load losses |
| India (BIS) | 98.50 | 5-star Bureau of Energy Efficiency rating, ambitious for smaller units |
| Australia | 99.15 | In line with AS 60076, incorporating EU Tier 2 equivalents |
Cost Breakdown and ROI: Basic 5 hp: $800-$1,500; Premium 20 hp VFD: $3,000-$6,000; Install: $500-$1,000; Maintenance: $100-$300/year. At 10% savings, $2,000 unit pays back in 18 months.
Cost by Power Rating
| Power Rating | Converter Type | Avg. Cost (USD) | Install Cost | ROI Period |
| 5 hp | Static | $800–$1,200 | $500 | 1 year |
| 10–20 hp | Rotary | $1,500–$3,000 | $700 | 12–18 months |
| 25–50 hp | Digital | $3,500–$6,000 | $1,000 | 18–24 months |
| 50+ hp | Premium Digital (Phase Perfect) | $6,000–$12,000 | $1,500 | 24+ months |
Conclusion
Single phase to three phase transformers are revolutionizing how businesses and individuals access and use power. They offer an efficient, cost-effective, and reliable way to bridge the gap between single-phase supply and three-phase demand—making advanced equipment accessible in more places than ever before. With global trends pushing for higher efficiency and smarter designs, these converters are set to play an even bigger role in the future of energy management. For long-term success, decision makers should select units that explicitly comply with IEC, IEEE, and NEMA standards, ensuring not just performance but also international acceptance and certification.
Whether you’re looking to power a workshop, expand a manufacturing line, or bring modern amenities to a remote location, understanding and leveraging single phase to three phase conversion can be your key to unlocking new productivity and efficiency. Evaluate your setup today for gains in sustainability and performance.
Frequently Asked Questions (FAQs)
Q1: Can I use a single phase to three phase transformer for all types of equipment?
A: Yes, most modern converters are suitable for home appliances, electric tools, and industrial motors. However, always check the power rating and compatibility with your specific equipment. Verify for high-precision gear needing extra filters.
Q2: How efficient are these converters?
A: High-quality converters can achieve up to 98% efficiency, thanks to advanced materials and intelligent design. Losses mainly from inversion; tops 98.7% in 2025 models.
Q3: What is the lifespan of a single phase to three phase transformer
A: With proper maintenance, expect a service life of 15–20 years for premium models. Up to 25 years with AI monitoring.
Q4: Is it better to upgrade to three-phase utility service or use a converter?
A: For many small businesses and rural users, converters are more cost-effective and easier to install than upgrading the entire electrical service. Converters for <50 hp; upgrades for scale.
Q5: Are there any limitations or downsides?
A: Some low-cost models may not handle heavy inductive loads well or may introduce harmonics. Choose a reputable brand and ensure the converter matches your load requirements. Not for >100 hp without paralleling; opt UL-listed.
Q6: How do I safely install one?
A: Follow NEC codes with GFCI breakers; professional install recommended for grounding and testing.
Q7: Which is the best single-phase to three-phase converter for CNC machines?
A: For CNC and precision equipment, converters like Phase Technologies or Phase Perfect are recommended due to <3% THD and stable voltage.
Q8: What is the price of a 10 hp single-phase to three-phase converter?
A: On average, a 10 hp rotary or digital converter costs between $1,500–$3,500 depending on brand and features.
Q9: How do advanced materials like Silicon Carbide (SiC) improve converter performance?
Modern high-end converters utilize SiC semiconductors and nanocrystalline cores, which reduce energy losses by up to 15% compared to traditional silicon steel. These materials allow for efficiencies exceeding 99% even at partial loads, ensuring cooler operation and higher power density.
Q10: What are the specific harmonic distortion limits for these converters?
To protect sensitive electronics and CNC machinery, high-quality digital converters must comply with IEEE 519 standards. This ensures that the Total Harmonic Distortion (THD) remains below 5%, preventing electrical noise from interfering with other devices on the same grid.
Q11: Can these converters be integrated with renewable energy systems?
Yes. Modern converters are designed to work seamlessly with solar and wind hybrids. They can help create off-grid three-phase microgrids, which, according to recent studies, can reduce reliance on diesel generators by up to 40%.
Q12: What is the impact of voltage imbalance on motor performance?
Voltage imbalance is a critical factor; even a 5% imbalance can increase motor winding temperatures by 25%, drastically shortening insulation life. High-quality converters maintain a Voltage Imbalance Ratio (VIR) below 2%, complying with IEC 61000-3-13 guidelines.
Reference
- https://www.carotron.com/articles/comparetransformers/
- https://www.ato.com/single-phase-to-3-phase-converter-working-principle
- https://www.carotron.com/articles/comparetransformers/
- https://journals.indexcopernicus.com/api/file/viewByFileId/154759
- https://www.clasp.ngo/wp-content/uploads/2021/01/SEAD-Distribution-Transformers-Report_Part-1_Comparison-of-Efficiency-Programs.pdf
Additional References for Updates: 7. IEEE Standards (2024). IEC 60076 Updates. 8. Future Market Insights (2025). Three Phase Green Power Transformer Market. 9. MDPI (2025). Design and Validation of a SiC-Based Single-to-Three-Phase Converter. 10. Energy Star (2025). Medium Voltage Distribution Transformers Scoping.