[latexpage]What Is an LED and How Does It Work?
An LED (Light Emitting Diode) is a small electronic component made from semiconductor material. When electricity flows through it, electrons meet “holes” in the material and release energy as light—a process called electroluminescence. Unlike old incandescent bulbs that waste energy as heat, LEDs stay cool, use less power, and last much longer.Why LEDs Are a Game-Changer
I distinctly recall exchanging a flickering incandescent bulb in my old apartment for an LED and being shocked that the LED stayed bright for years. If you swap out an incandescent for an LED, you are going to see a massive electricity savings. LED bulbs are highly efficient, using most of the electricity they consume to produce light rather than converting most of it to heat. A 60-watt incandescent bulb can produce 800 lumens and it may take 8-10 watts of an LED to produce the same light. That’ll translate to a significant savings on your electricity bill! LED’s are also very durable. They are solid state devices, which means while glass bulbs are very fragile, light emitting diode can take a bit of a bump without breaking. And, they last 25,000 hours or more, or about 25 times the 1,000 hours of an incandescent bulb. It’s no wonder LED’s have become the gold standard in everything from home lighting to car headlights.
Beyond the Home: LEDs in Cool Applications
LEDs aren’t only used to make your living room pretty. They have made their way into some pretty interesting applications. For starters, in hospitals, UV LEDs have been shown to disinfect equipment because they have a high germ-killing mechanism. In agriculture, UV and specialized LEDs can replace sunlight with features to make plants thrive indoors. I recently read about a vertical farm that used red and blue LEDs and increased crop yield by 30%. Not too shabby for a little diode either! Then there are displays, giant loud LED billboards such as Times Square or stadium scoreboards rely on a lot of different combinations of red, green, and blue LEDs to create images. We have also seen LEDs used in art and design for dynamic installations that can turn spaces into experiences. LEDs are amazing because they can produce a variety of colors. By changing the semiconductor materials, manufacturers can create light at any point in the light spectrum, from infrared for remote controls to ultraviolet for sterilization. Do you wonder why your TV remote actually works? It’s a signal generated by an light emitting diode using infrared light. As for the bright blue LEDs in your gaming setup? Those are most likely made using gallium nitride, which made white LEDs possible when it was invented in the 1990’s. This ability to create colors allows for endless possibilities with LEDs. Take automotive lighting for example; white LEDs produce bright, crisp headlights while red LEDs can be used for taillights ensuring a driver can see the light but still not be blinded.
LEDs are amazing because they can produce a variety of colors. By changing the semiconductor materials, manufacturers can create light at any point in the light spectrum, from infrared for remote controls to ultraviolet for sterilization. Do you wonder why your TV remote actually works? It’s a signal generated by an light emitting diode using infrared light. As for the bright blue LEDs in your gaming setup? Those are most likely made using gallium nitride, which made white LEDs possible when it was invented in the 1990’s. This ability to create colors allows for endless possibilities with LEDs. Take automotive lighting for example; white LEDs produce bright, crisp headlights while red LEDs can be used for taillights ensuring a driver can see the light but still not be blinded.Choosing the Right LED for You
With so many different types of LED bulbs and devices available, picking one can be overwhelming. When choosing an LED, begin by checking the lumens (brightness), not the watts; LEDs are less power-hungry and provide the same amount of brightness. For indoor home lighting, warm white (2700-3000K) creates a cozy atmosphere, while cool white (4000K +) is for an office or kitchen. If you like smart lighting, LIFX offers a range of LEDs that can be controlled with your phone for changing colors for mood settings.
Introduction to LEDs (Light Emitting Diodes)
A Light Emitting Diode (LED) is a semiconductor p–n junction diode that produces light through a process called electroluminescence when it is forward biased. In simple terms, an LED converts electrical energy directly into light when electrons recombine with holes inside the semiconductor material. This direct energy conversion makes LEDs far more efficient than traditional incandescent bulbs. While incandescent lamps waste most of their energy as heat, LEDs generate minimal heat, achieve up to 90% higher energy efficiency, and typically offer a lifespan exceeding 50,000 hours. This is why small indicator LEDs in televisions can remain illuminated for years without burning out, and modern LED bulbs stay cool even after extended use.
What you’ll learn
In this guide, you’ll discover how LEDs work, their advantages and drawbacks, technical specifications like CRI and efficacy, and real-world applications. Whether you’re a student, engineer, or just curious, this will give you a complete understanding of LEDs. How LEDs create light in a unique way. The key performance factors: luminous efficacy, CRI, and L70. The main types of LEDs and where they are used. Everyday applications and the pros and cons . How to pick the right LED for your home or projectWhat Is an LED and How Does It Work?
An LED (Light Emitting Diode) is a small electronic component made from semiconductor material. When electricity flows through it, electrons meet “holes” in the material and release energy as light—a process called electroluminescence. Unlike old incandescent bulbs that waste energy as heat, LEDs stay cool, use less power, and last much longer.The LED Design Equation: To prevent an LED from burning out, you must calculate the current-limiting resistor ($R$) using Ohm’s Law: $$R = \frac{V_{source} – V_{forward}}{I_{forward}}$$
- $V_{source}$: Your power supply voltage (e.g., 5V).
- $V_{forward}$ ($V_f$): The voltage “drop” of the LED (typically 1.8V for Red, 3.2V for Blue/White).
- $I_{forward}$ ($I_f$): The desired current (usually 0.02A or 20mA for standard LEDs).
How LEDs Are Made
An LED is like a tiny semiconductor sandwich:- One side (n-type) has extra electrons.
- The other side (p-type) has spaces (holes) for electrons.
- When powered by a direct current (DC), electrons flow from the n-type side to the p-type side. When they meet a hole, they release energy in the form of light.
- The color of the light depends on the materials used in the semiconductor. For example, gallium arsenide creates red light, while gallium nitride creates blue light.
Key LED Performance Metrics
- Luminous efficacy (lm/W): This measures how much light you get for every watt of electricity. LEDs are incredibly efficient, reaching 75–200 lm/W compared to only 10–17 lm/W for incandescent bulbs.
- Color Rendering Index (CRI): This indicates how accurately the light shows colors. A higher CRI (80–90+) means colors look more natural. Good CRI: 80+ | Great CRI: 90+.
- Lumen maintenance (L70): This is the time it takes for an LED to dim to 70% of its original brightness, typically 25,000–50,000 hours.
Professional Standards:
- IES LM-79: Measures initial photometric and electrical performance.
- IES LM-80: Measures lumen depreciation over time to predict lifespan.
- McAdam Ellipse: Used in “Binning” to ensure color consistency across a batch of LEDs.
Why LEDs Are a Game-Changer
I distinctly recall exchanging a flickering incandescent bulb in my old apartment for an LED and being shocked that the LED stayed bright for years. If you swap out an incandescent for an LED, you are going to see a massive electricity savings. LED bulbs are highly efficient, using most of the electricity they consume to produce light rather than converting most of it to heat. A 60-watt incandescent bulb can produce 800 lumens and it may take 8-10 watts of an LED to produce the same light. That’ll translate to a significant savings on your electricity bill! LED’s are also very durable. They are solid state devices, which means while glass bulbs are very fragile, light emitting diode can take a bit of a bump without breaking. And, they last 25,000 hours or more, or about 25 times the 1,000 hours of an incandescent bulb. It’s no wonder LED’s have become the gold standard in everything from home lighting to car headlights.How LEDs Are Made: A Peek Behind the Scenes
Ever wonder how these little light makers are made? LED chips begin as a semiconductor wafer, usually made from gallium arsenide or indium gallium nitride. Manufacturers ‘dope’ the semiconductor with desired impurities to create the n-type and p-type regions. They then stack these layers to form a p-n junction, where the magic of light happens. It then gets encased in a clear epoxy dome shape, which protects the chip and directs the light emission outwards. Essentially creating a precious little gemstone that lights up when it receives power. Cool fun fact, the shape of the dome is critical to direct the light. They are great for direction lighting applications such as spot lights or task lamps!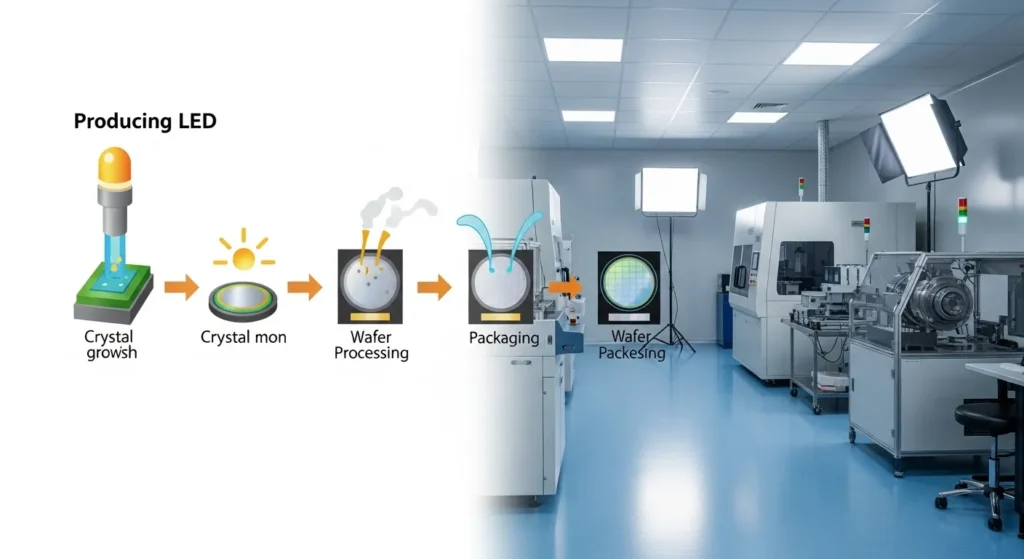
Everyday Uses: Where You’ll Spot LEDs
LEDs are everywhere! It’s difficult to look anywhere without seeing them once you start noticing them. The bulbs in your home are most likely diode emitting light, on the lamps, in the under-cabinet strips, and even on the backlighting of your TV. When you step outside you can see them in streetlights, traffic signs, and car tail lights. They are even present in your phone for the display, or used as flash for your selfies. One user on Reddit claimed they replaced every bulb in their home with LEDs purchased from Philips and saw their power bill decrease by almost 20%! These kinds of findings indicate that LEDs offer a viable option to those wishing to save energy without sacrificing brightness.| Type of LED | Main Uses |
| Indicator LEDs | Power/status indicators on electronics |
| High-Power LEDs | Flashlights, car headlights, street lights |
| SMD LEDs | LED strips, compact light fixtures |
| COB LEDs | High-brightness panels, industrial lighting |
| OLEDs | Smartphone and TV screens |
Beyond the Home: LEDs in Cool Applications
LEDs aren’t only used to make your living room pretty. They have made their way into some pretty interesting applications. For starters, in hospitals, UV LEDs have been shown to disinfect equipment because they have a high germ-killing mechanism. In agriculture, UV and specialized LEDs can replace sunlight with features to make plants thrive indoors. I recently read about a vertical farm that used red and blue LEDs and increased crop yield by 30%. Not too shabby for a little diode either! Then there are displays, giant loud LED billboards such as Times Square or stadium scoreboards rely on a lot of different combinations of red, green, and blue LEDs to create images. We have also seen LEDs used in art and design for dynamic installations that can turn spaces into experiences.The Colorful World of LEDs
 LEDs are amazing because they can produce a variety of colors. By changing the semiconductor materials, manufacturers can create light at any point in the light spectrum, from infrared for remote controls to ultraviolet for sterilization. Do you wonder why your TV remote actually works? It’s a signal generated by an light emitting diode using infrared light. As for the bright blue LEDs in your gaming setup? Those are most likely made using gallium nitride, which made white LEDs possible when it was invented in the 1990’s. This ability to create colors allows for endless possibilities with LEDs. Take automotive lighting for example; white LEDs produce bright, crisp headlights while red LEDs can be used for taillights ensuring a driver can see the light but still not be blinded.
LEDs are amazing because they can produce a variety of colors. By changing the semiconductor materials, manufacturers can create light at any point in the light spectrum, from infrared for remote controls to ultraviolet for sterilization. Do you wonder why your TV remote actually works? It’s a signal generated by an light emitting diode using infrared light. As for the bright blue LEDs in your gaming setup? Those are most likely made using gallium nitride, which made white LEDs possible when it was invented in the 1990’s. This ability to create colors allows for endless possibilities with LEDs. Take automotive lighting for example; white LEDs produce bright, crisp headlights while red LEDs can be used for taillights ensuring a driver can see the light but still not be blinded.Pros and Cons: What’s the Real Deal?
LEDs have a lot going for them, but let’s be real no tech is perfect. Here’s a quick rundown:- Pros: Energy-efficient, long-lasting, durable, and available in many colors. They’re eco-friendly, with no mercury (unlike some fluorescent lamps), and they produce minimal heat.
- Cons: Upfront costs can be higher than traditional bulbs, though prices have dropped significantly. Some LEDs can flicker if paired with incompatible dimmers, which can be annoying.
Advanced Troubleshooting:
- Problem: LED glows when the switch is OFF. Cause: Ghosting from leakage current in smart switches.
- Problem: LED flickers on camera. Cause: PWM frequency mismatch with camera shutter speed.
- Problem: Dimming over time. Cause: Thermal droop (excessive junction temperature).